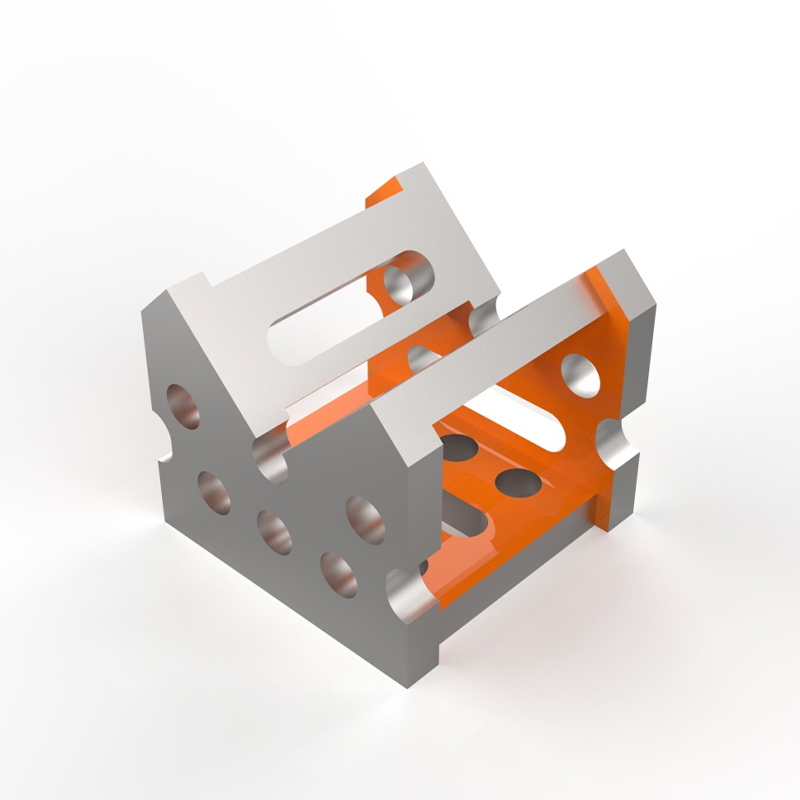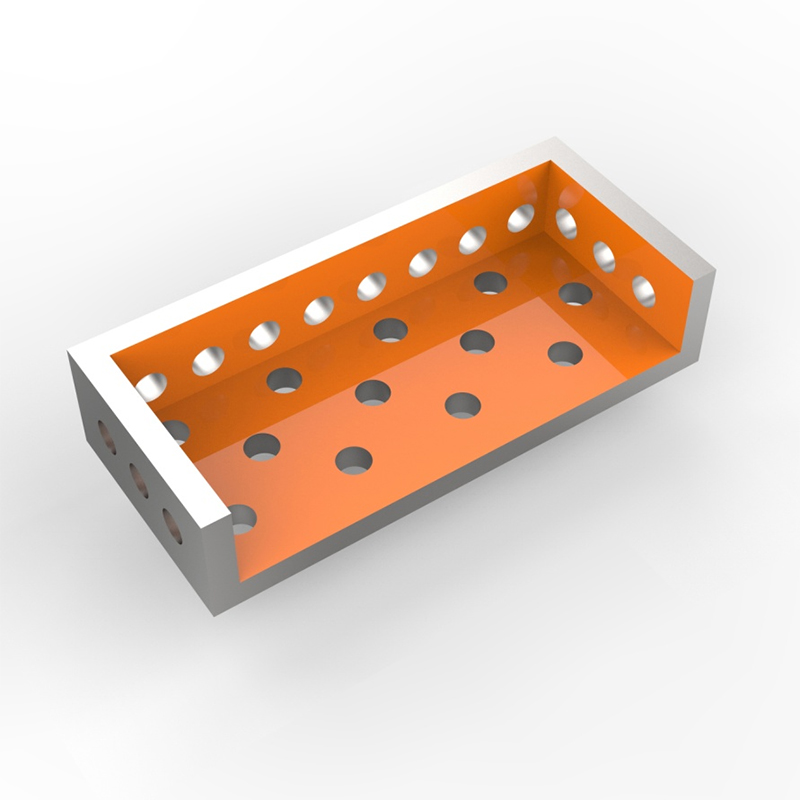

This comprehensive guide explores the crucial aspects of designing and implementing effective welding fixtures. We'll cover fixture types, design considerations, material selection, and best practices for ensuring consistent, high-quality welds. Learn how to optimize your welding fixture for improved efficiency and reduced costs.
In welding processes, a welding fixture is an essential tool. It's a device used to hold and accurately position parts during welding, ensuring consistent weld quality and repeatability. Without a well-designed fixture, you risk inconsistencies in weld placement, leading to defects and potentially compromising the structural integrity of the final product. A properly designed welding fixture minimizes distortion, increases productivity, and ultimately reduces costs. This is especially critical in high-volume production environments.
Clamp-type fixtures are a common choice, offering versatility and ease of use. They use clamps to secure the workpieces, allowing for quick setup and adjustment. However, they may not be suitable for all applications, especially those requiring extremely high precision.
Jig-type fixtures offer superior accuracy and repeatability compared to clamp-type fixtures. They usually incorporate locating pins and bushings to accurately position the components. This makes them ideal for complex assemblies requiring precise weld placement.
Magnetic fixtures are useful for holding ferrous materials, offering a quick and convenient method for securing workpieces. However, they may not be suitable for all applications, and the magnetic force may need to be carefully considered to prevent workpiece movement during the welding process. Additionally, their holding force can be affected by factors like material thickness and the presence of interfering materials.
The design of your welding fixture is paramount. Key considerations include:
Choosing the right material is crucial. Common materials include steel (for its strength and durability), aluminum (for its lightweight nature), and specialized materials like cast iron for enhanced vibration damping. The material's properties, such as thermal conductivity and dimensional stability, must be carefully considered in relation to the welding process being used. For example, a material with high thermal conductivity may be preferred for processes that generate significant heat.
Effective welding fixtures incorporate several key design principles: rigid construction to prevent deformation under load, strategically placed clamping points to securely hold the components without inducing stress, and accurate locating features to ensure precise alignment of the workpieces. The design should also consider accessibility for the welder and ease of loading and unloading components.
Selecting the appropriate welding fixture depends heavily on factors such as the type of welding process, the complexity of the assembly, the production volume, and budget constraints. Consulting with experienced welding fixture designers or manufacturers like Botou Haijun Metal Products Co., Ltd. can be invaluable in making the right decision.
Regular maintenance and proper use extend the life of your welding fixture and ensure its continued accuracy. This includes regular inspection for wear and tear, cleaning to remove weld spatter, and lubrication of moving parts. Following established safety procedures during operation is also crucial.
While investing in a welding fixture involves upfront costs, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial expense. The improved quality, increased productivity, and reduced scrap rates contribute significantly to a positive ROI. Accurate cost analysis, considering both initial investment and operational savings, is vital in evaluating the economic feasibility of a welding fixture project.
| Fixture Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Clamp-Type | Versatile, easy to use, relatively inexpensive | Lower accuracy, may not be suitable for high-precision applications |
| Jig-Type | High accuracy, excellent repeatability | More complex design, higher cost |
| Magnetic | Quick setup, convenient for ferrous materials | Limited holding force, not suitable for all applications |
This guide provides a foundational understanding of welding fixtures. Remember to consult relevant industry standards and best practices for specific applications. The information provided here is for general guidance only and should not be considered professional advice. For specific design requirements, contact a qualified engineer or welding fixture manufacturer.