Understanding and Utilizing U-Shaped Square Boxes
This comprehensive guide explores the design, applications, and manufacturing considerations of U-shaped square boxes. We'll cover various aspects, from understanding their unique geometry to exploring their diverse uses across multiple industries. Learn how to choose the right material, dimensions, and manufacturing process for your specific needs. Whether you're a designer, engineer, or simply curious, this article provides a detailed overview of U-shaped square boxes.
What is a U-Shaped Square Box?
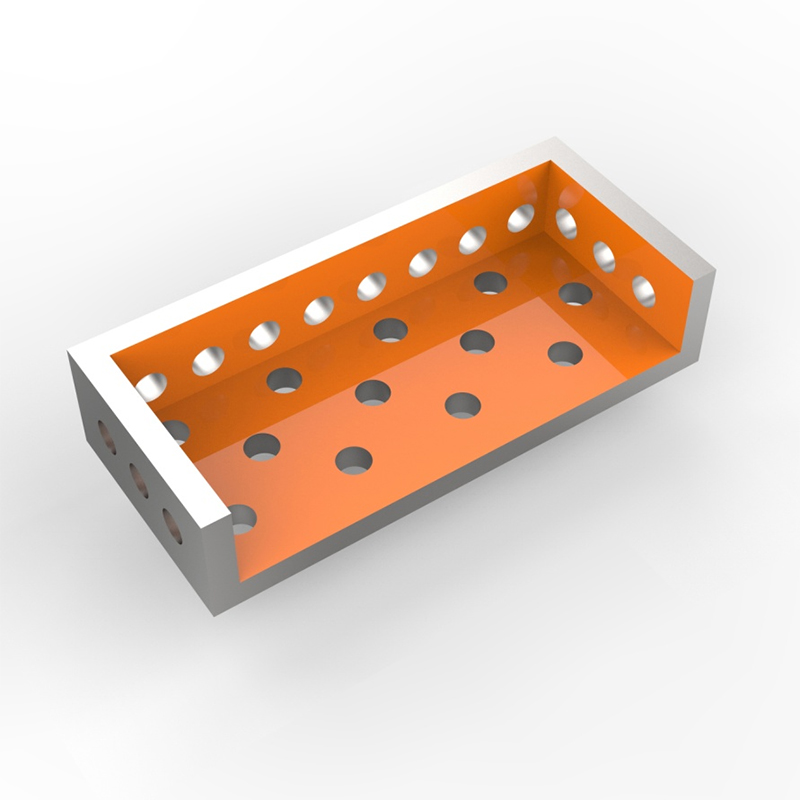
A U-shaped square box, also sometimes referred to as a U-channel or U-section, is a type of structural element characterized by its open, U-shaped profile with square cross-section. Unlike a completely enclosed box, it has an open top, allowing for easy insertion of materials or components. This unique design offers a combination of strength and flexibility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. The dimensions, material, and manufacturing processes can be customized to meet specific requirements.
Materials Used in U-Shaped Square Box Manufacturing
The material choice for a U-shaped square box significantly impacts its strength, durability, and cost. Common materials include:
- Steel: Offers high strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Different grades of steel are available, each offering varying properties.
- Aluminum: A lightweight yet strong option, suitable for applications where weight reduction is a priority. Aluminum is also corrosion-resistant.
- Stainless Steel: Provides superior corrosion resistance, making it suitable for use in harsh environments or applications requiring hygiene, such as the food industry.
- Plastics: Various plastics, such as ABS or PVC, offer cost-effective solutions for less demanding applications. They can be easily molded into complex shapes.
Applications of U-Shaped Square Boxes
The versatility of U-shaped square boxes makes them suitable for a wide array of applications across diverse industries. Some examples include:
- Packaging: Protecting and organizing smaller items during shipping and handling. Consider custom U-shaped square boxes from Botou Haijun Metal Products Co., Ltd. for robust and reliable packaging solutions.
- Structural Components: Used as framing elements in various structures, providing strength and support.
- Machinery Components: Incorporated into machinery for guidance, support, or protection of other components.
- Automotive Industry: Used in automotive parts and assembly.
- Electronics Industry: Providing structural support for electronic components.
Manufacturing Processes for U-Shaped Square Boxes
Several manufacturing processes can be used to create U-shaped square boxes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Press Bending: A common method for bending sheet metal into the desired U-shape.
- Extrusion: Creates continuous lengths of U-shaped square box profiles from a molten material.
- Casting: Suitable for complex shapes and various materials.
- 3D Printing: Enables rapid prototyping and customization, particularly useful for smaller production runs.
Choosing the Right U-Shaped Square Box: Key Considerations
Selecting the appropriate U-shaped square box requires considering several factors:
- Material: The strength, durability, and corrosion resistance required.
- Dimensions: The specific size and shape needed to accommodate the intended application.
- Manufacturing Process: Balancing cost, production volume, and desired tolerances.
- Surface Finish: Required for aesthetics, corrosion protection, or specific functional requirements.
Comparison of Common Materials
| Material | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Cost | Weight |
| Steel | High | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Aluminum | High | Excellent | High | Low |
| Stainless Steel | High | Excellent | High | High |
| Plastics | Low to Moderate | Variable | Low | Low |
This information should provide a solid foundation for understanding and utilizing U-shaped square boxes in various applications. Remember to always consider the specific requirements of your project when making material and manufacturing decisions.