
This comprehensive guide explores the critical aspects of designing and implementing robot welding fixtures, covering everything from initial design considerations to final fixture implementation and maintenance. We'll delve into fixture types, material selection, design best practices, and common pitfalls to avoid, ensuring you can create robust and efficient fixtures for your robotic welding applications. Learn how to optimize your welding process and improve overall productivity.
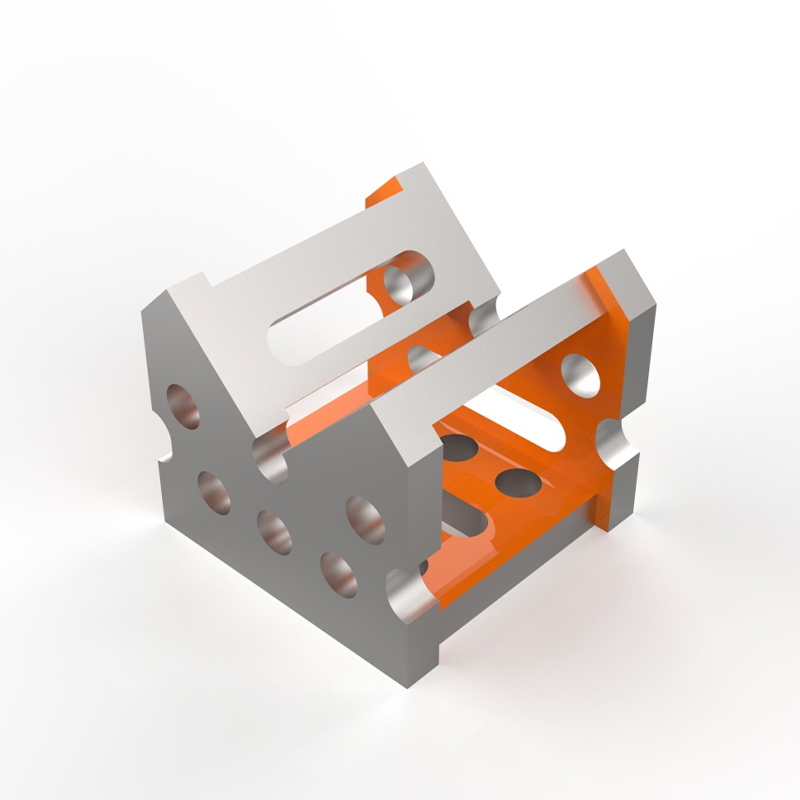
Robot welding fixtures are indispensable in automated welding processes. They provide precise part positioning and hold the workpiece securely during welding, ensuring consistent weld quality and repeatability. Without them, robotic welding becomes significantly less accurate and efficient. Proper fixturing eliminates the need for manual manipulation, leading to increased throughput and reduced labor costs. The choice of fixture significantly impacts the efficiency and success of your robotic welding operation.
Several types of robot welding fixtures cater to different applications and welding processes. Common types include:
Effective fixture design requires careful consideration of several factors:
The choice of material for your robot welding fixtures directly impacts their durability, cost, and performance. Here's a comparison of common materials:
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | High strength, rigidity, and durability | Can be heavier and more expensive than other materials |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and good thermal conductivity | Lower strength than steel, may require more robust designs |
Precise installation and calibration are crucial for accurate robotic welding. This process typically involves aligning the fixture with the robot's coordinate system and verifying the workpiece's position.
Regular maintenance, including cleaning, lubrication, and inspection, extends the life of your robot welding fixtures. Addressing any issues promptly prevents costly downtime.
For high-quality metal products and expert manufacturing solutions, consider partnering with Botou Haijun Metal Products Co., Ltd. Their expertise in precision metal fabrication can significantly enhance your robot welding fixtures' performance.
Disclaimer: This information is for general guidance only and does not constitute professional engineering advice. Always consult with qualified professionals for specific design and implementation needs.